The US labor market is a cornerstone of the country’s economic vitality. As one of the world’s largest economies, analyzing the US growth jobs ratio offers critical insights into economic performance, employment trends, and future workforce strategies. This article dives deep into the factors influencing job growth, the relationship between economic expansion and employment, and how policymakers and businesses adapt to changing labor market dynamics.
Introduction
The US growth jobs ratio measures the pace at which jobs are created relative to economic growth, providing a snapshot of the labor market’s health. Understanding this metric is vital for policymakers, economists, and job seekers. It sheds light on key areas like job creation, unemployment, and workforce participation, all of which are critical for sustaining long-term economic prosperity.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll analyze how the US growth jobs ratio is shaped by factors like GDP growth, industry trends, and labor force participation. We’ll also explore key US labor market trends, delve into job creation data, and discuss the outlook for employment in America.
Economic Growth and Employment
Economic growth and employment are deeply interconnected. When GDP expands, it typically spurs job creation as businesses grow and invest in labor. However, this relationship is not always linear. For instance:
- A rapid increase in GDP may not lead to proportional employment gains due to automation or outsourcing.
- Conversely, slower economic growth could still sustain steady employment gains if industries like healthcare and technology experience structural growth.
The GDP and job growth correlation provides a foundation for analyzing the efficiency of job creation in response to economic expansion. In the US, industries like technology, healthcare, and renewable energy have shown significant contributions to employment, even during periods of slower GDP growth.
US Labor Market Trends
The American labor market is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, demographic shifts, and global economic changes. Notable US labor market trends include:
- Increased labor force participation rate among women and minorities.
- A growing emphasis on remote and flexible work arrangements.
- Demand for tech-based and green energy jobs outpacing traditional industries like manufacturing.
These trends highlight the need for workers to adapt to changing job markets and acquire new skills that align with emerging industries.
Job Creation Statistics USA
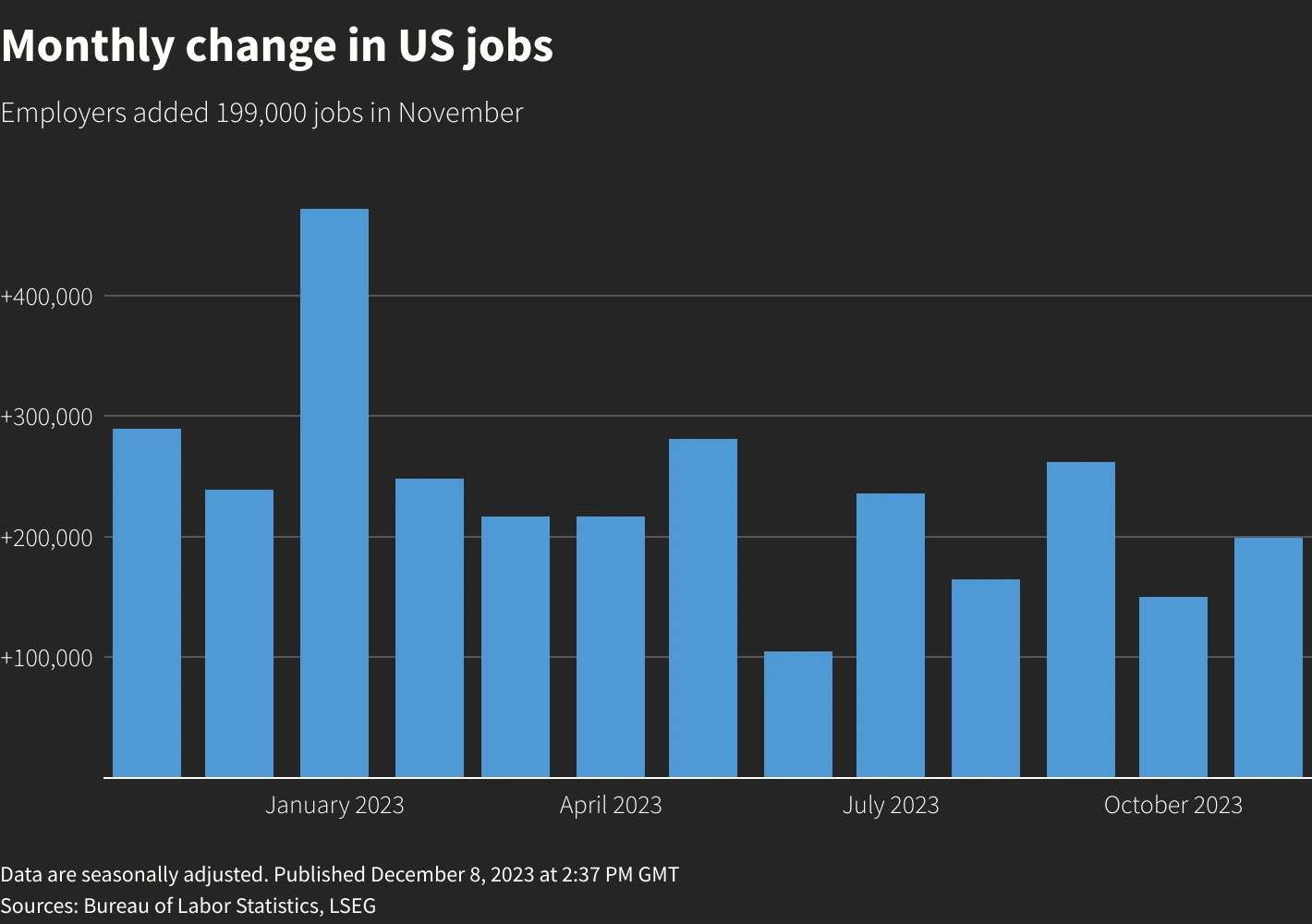
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), job creation has remained resilient despite challenges like the pandemic and inflationary pressures. Recent job creation statistics USA show robust growth in sectors like healthcare, technology, and leisure, while manufacturing and retail face headwinds.
Key figures include:
- Monthly non-farm payroll employment data, which highlights how many jobs are added or lost in the private and public sectors.
- The private sector job growth rate, which outpaces public sector employment in most months.
Employment-to-Population Ratio
The employment-to-population ratio measures the proportion of working-age Americans currently employed. This ratio is critical for understanding the inclusiveness and health of the labor market.
While the employment-to-population ratio has rebounded since the COVID-19 pandemic, it has not yet reached pre-pandemic levels due to factors like early retirements and shifting workforce priorities.
US Workforce Growth Rate
The US workforce growth rate reflects the expansion of the labor force, which includes all individuals actively employed or seeking employment. A robust growth rate indicates a healthy pipeline of talent entering the market, while a slower rate may signal demographic challenges or a mismatch in skills.
Demographics play a significant role in shaping workforce growth. For example, the aging baby boomer population has contributed to a shrinking labor force, while younger generations are entering industries with a focus on technology and sustainability.
Unemployment Rate in the US
The unemployment rate in the US remains a key indicator of labor market health. A low unemployment rate typically signals strong economic conditions, but it’s important to consider underemployment and job quality as well.
Recent reports show that unemployment has remained below 4%, indicating a tight labor market. However, disparities persist across different demographic groups and regions, underscoring the need for targeted policies to address inequality.
Job Market Recovery USA
The job market recovery USA post-pandemic has been impressive, with millions of jobs regained since the initial downturn. However, challenges such as inflation, global uncertainty, and supply chain disruptions continue to affect certain sectors.
Industries like travel, hospitality, and healthcare have led the recovery, while sectors like retail and manufacturing still face hurdles due to structural shifts in consumer behavior.
Labor Force Participation Rate
The labor force participation rate measures the percentage of working-age individuals who are employed or actively seeking work. This metric highlights trends in workforce engagement and offers insights into barriers like childcare, education, or health issues that may prevent people from working.
Recent trends show a gradual rebound in labor force participation, particularly among women re-entering the workforce after pandemic-related disruptions.
Job Openings vs. Job Seekers USA
The ratio of job openings vs. job seekers USA is another critical indicator of labor market dynamics. As of 2024, the US has more job openings than job seekers, highlighting a tight labor market.
This gap reflects a mismatch between the skills employers seek and the qualifications of job seekers. Investments in education, training, and upskilling are essential to bridging this divide.
Wage Growth and Employment
Wage growth and employment are intricately linked, with rising wages signaling increased demand for labor. However, excessive wage growth can also lead to inflationary pressures.
In the current labor market, wages have increased significantly in sectors like technology and healthcare, while low-wage industries have struggled to attract talent without competitive pay.
US Employment Growth Sectors
Certain industries have consistently driven US employment growth sectors, including:
- Healthcare: Aging populations and increased health awareness.
- Technology: Demand for AI, cybersecurity, and software development.
- Green energy: Expansion of renewable energy jobs like solar and wind installation.
Understanding these trends helps policymakers and job seekers align strategies for future growth.
Federal Reserve Employment Analysis
The Federal Reserve employment analysis plays a critical role in shaping monetary policy. By assessing the labor market’s strength, the Fed adjusts interest rates to balance inflation and job growth.
Recent Fed actions have aimed to curb inflation without significantly impacting job creation, demonstrating the delicate balance required in policymaking.
Part-Time vs. Full-Time Employment Trends
The debate over part-time vs. full-time employment trends sheds light on workforce preferences and economic constraints. While full-time employment remains the norm, part-time roles have grown due to the rise of gig work and flexible schedules.
This trend is particularly evident in younger workers and those balancing caregiving responsibilities.
Long-Term Job Growth USA
Long-term job growth USA is shaped by megatrends like automation, climate change, and demographic shifts. Over the next decade, jobs in technology, healthcare, and clean energy are expected to dominate growth, while traditional roles in manufacturing and retail may decline.
Conclusion
The US growth jobs ratio provides invaluable insights into the health and dynamics of the American labor market. From the relationship between economic growth and employment to trends like wage growth and industry-specific gains, this ratio captures a holistic picture of where the workforce is headed.
To maintain robust job growth, policymakers and businesses must invest in education, reskilling programs, and equitable workforce policies that address disparities in employment opportunities. By focusing on high-growth sectors and adapting to changing labor market trends, the US can sustain a thriving economy and a resilient workforce.
For more interesting blogs, visit our site: https://futuretrendz.co.uk/
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the US growth jobs ratio?
The US growth jobs ratio measures the pace of job creation relative to economic growth, providing insights into labor market efficiency.
2. Which industries drive US employment growth?
Key growth sectors include healthcare, technology, and renewable energy, which consistently outpace traditional industries like manufacturing.
3. How does wage growth affect employment?
Wage growth signals labor demand but can also lead to inflationary pressures if it outpaces productivity.
4. What is the role of the Federal Reserve in employment?
The Federal Reserve analyzes labor market trends to adjust monetary policy, balancing inflation and job growth.
5. What are the long-term trends in the US labor market?
Automation, climate change, and demographic shifts are reshaping the labor market, with a focus on tech and sustainable jobs.